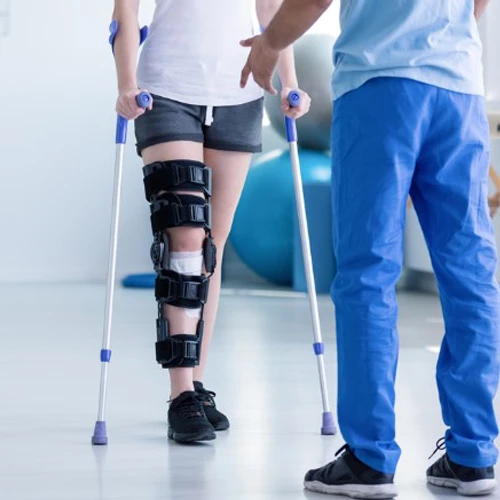
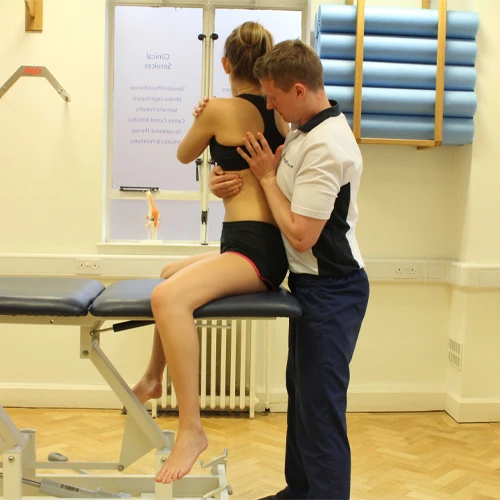
Pre and Post Surgical Rehabilitation refers to the strategies, exercises, and treatments provided before and after surgery to optimize recovery, reduce complications, and ensure the best possible outcome. The goal is to prepare the body for surgery, facilitate healing after the procedure, and restore function and mobility as quickly and safely as possible.
Pre-Surgical Rehabilitation (Prehabilitation)
Prehabilitation focuses on preparing the body and mind for surgery, with the aim of improving the surgical outcome and speeding up recovery. It is particularly important in elective surgeries (e.g., joint replacements, spine surgery) but can also benefit individuals undergoing trauma-related surgeries.
Key Components of Pre-Surgical Rehabilitation:
-
Physical Conditioning:
- Strengthening: Strengthening the muscles surrounding the affected joint or area can help protect it during surgery and improve post-surgical recovery. For example, strengthening the muscles around the knee before knee surgery (like a knee replacement or ACL reconstruction) helps support healing afterward.
- Range of Motion: Improving flexibility and range of motion can ensure that the area is more mobile post-surgery and may reduce stiffness after the procedure.
-
Pain Management:
- Addressing any pain or discomfort before surgery can make the recovery period smoother. Techniques like ice, heat therapy, and gentle stretching may be used in prehab.
-
Education:
- Providing information about what to expect during and after surgery helps reduce anxiety and prepares patients for the recovery process. This includes setting realistic expectations, explaining post-surgical restrictions, and teaching techniques for early rehabilitation.
-
Mental and Emotional Preparation:
- Surgery can be a stressful experience. Prehab often includes mental conditioning to prepare for the emotional and psychological challenges of surgery and recovery. This could include relaxation techniques, meditation, or stress management strategies.
-
Improving Mobility and Functional Capacity:
- Teaching patients safe movement techniques, fall prevention strategies, and simple functional exercises can be essential, especially for older adults or those undergoing orthopedic surgeries like hip or knee replacements.
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
Post-surgical rehabilitation is the process that begins immediately after surgery and continues until the individual has recovered and returned to normal function. The exact rehabilitation program depends on the type of surgery, the extent of the injury or disease, and the individual’s overall health.
Key Components of Post-Surgical Rehabilitation:
-
Pain Control:
- Managing pain is a primary concern immediately after surgery. This may involve medications, ice, elevation, and gentle movements. Effective pain management allows for better engagement in rehabilitation exercises and prevents complications due to inactivity.
-
Restoration of Range of Motion (ROM):
- After surgery, especially joint surgeries (e.g., knee, hip, shoulder), the goal is to restore the normal range of motion. Gentle stretching and joint mobilizations are introduced gradually to avoid stiffness and improve movement.
-
Strengthening:
- Once healing has progressed, targeted strengthening exercises are introduced to rebuild muscle strength, improve function, and support the surgical site. This is especially important after surgeries like joint replacements, ligament repairs, or spine surgeries.
-
Mobility and Gait Training:
- Following surgeries involving the lower body (e.g., knee, hip, ankle), gait training is often necessary to ensure a safe and efficient walking pattern. This may include the use of assistive devices like crutches, walkers, or canes early in recovery.
-
Functional Training:
- Aimed at helping the patient regain the ability to perform daily activities (e.g., getting in and out of a chair, climbing stairs, dressing). This aspect of rehabilitation helps the individual return to their pre-surgery lifestyle and re-engage in work or recreational activities.
-
Scar Management and Soft Tissue Mobilization:
- Scar tissue can cause tightness or discomfort post-surgery. Physical therapists use various manual therapies, massage, and specific exercises to manage scar tissue and improve tissue mobility. This can prevent adhesions and improve overall function.
-
Psychological Support:
- Post-surgery recovery can be challenging both physically and emotionally. Addressing mood changes, anxiety, or depression, and providing support during recovery is essential. Positive reinforcement and setting achievable goals can help with motivation.
-
Gradual Return to Activity:
- Reintroducing normal activities gradually is important to prevent overuse injuries or re-injury. Whether it’s work, sports, or other activities, the rehabilitation plan includes a structured progression back to full function, avoiding premature stress on the surgical area.
-
Ongoing Monitoring and Adaptation:
- As recovery progresses, rehabilitation plans are adjusted based on the individual’s needs. This includes progressing from basic exercises to more advanced activities and functional tasks as strength and mobility improve.
Goals of Pre and Post-Surgical Rehabilitation:
- Prehabilitation Goals:
- Prepare the body for surgery by improving strength, flexibility, and function.
- Reduce post-surgical complications and speed up recovery.
- Educate and emotionally prepare the patient for surgery.
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation Goals:
- Minimize pain and swelling.
- Restore mobility, strength, and function to pre-surgical levels (or better).
- Prevent complications such as blood clots, joint stiffness, or muscle weakness.
- Improve the overall quality of life and return to normal daily activities as soon as possible.
Benefits:
- Faster Recovery: Prehabilitation can reduce the time needed to recover from surgery by enhancing physical conditioning and preparing the body for the stresses of surgery.
- Reduced Complications: Proper rehabilitation reduces the risk of complications, such as infection, muscle atrophy, or joint stiffness.
- Improved Functional Outcomes: Effective rehabilitation leads to better functional outcomes post-surgery, allowing patients to return to normal activities or sports more quickly and with less risk of re-injury.
Pre and post-surgical rehabilitation is a critical part of the recovery journey, helping patients optimize outcomes, reduce recovery time, and enhance long-term function and quality of life.