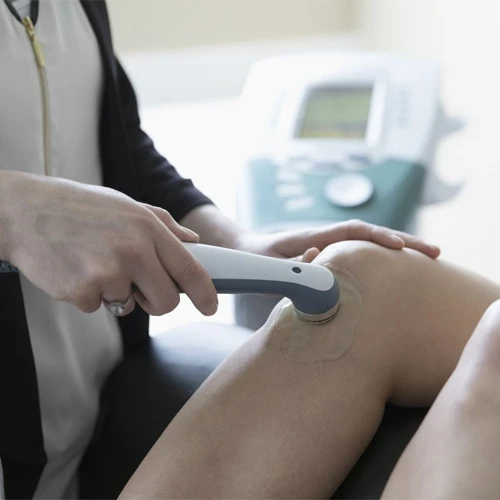
Physical modalities are therapeutic techniques that use physical agents or interventions to treat various musculoskeletal conditions, manage pain, reduce inflammation, promote healing, and improve functional mobility. These modalities can be applied alone or in combination with other therapeutic interventions such as exercises, manual therapy, or patient education. They are commonly used in physical therapy, chiropractic care, and rehabilitation settings.
Physical modalities can be categorized into several types based on their application and therapeutic effects. Below is a description of the main types:
1. Thermal Modalities
a. Heat Therapy
Heat is used to relax muscles, improve circulation, and increase flexibility. It can be applied in various forms, such as:
- Hot packs: Moist or dry heat applied to the skin.
- Paraffin baths: Wax that is heated and applied to hands or feet.
- Infrared lamps: A heat source that penetrates the skin to warm tissues.
- Heating pads: Used at home or in clinical settings for muscle relaxation.
Indications for heat therapy:
- Chronic pain or stiffness
- Muscle spasms
- Joint stiffness
- Tissue healing (after the acute phase has passed)
b. Cold Therapy (Cryotherapy)
Cold therapy is used to reduce inflammation, numb pain, and decrease swelling. It works by constricting blood vessels, which reduces blood flow to the injured area. Methods include:
- Ice packs or cold compresses: Applied directly to the affected area.
- Ice massage: Rubbing ice directly on the skin.
- Cold baths or cryo-cuffs: Used for larger areas like joints.
Indications for cold therapy:
- Acute injuries (sprains, strains)
- Swelling and inflammation
- Post-surgical recovery
- Pain management (especially for acute injuries)
2. Electrical Modalities
a. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
TENS uses low-voltage electrical currents to reduce pain. Electrodes are placed on the skin near the painful area to stimulate nerves and block pain signals.
Indications for TENS:
- Acute and chronic pain management (e.g., back pain, arthritis)
- Neuropathic pain
- Post-surgical pain
b. Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES)
NMES involves electrical stimulation to stimulate muscle contraction, which can help with muscle strengthening, prevent atrophy, and improve circulation. It is often used in rehabilitation after injury or surgery.
Indications for NMES:
- Muscle weakness (post-injury or post-surgery)
- Preventing muscle atrophy
- Improving muscle function after neurological disorders (e.g., stroke, spinal cord injury)
c. Interferential Current Therapy (IFC)
IFC uses medium-frequency electrical currents to target deeper tissues while minimizing discomfort. It is often used for pain relief and muscle stimulation.
Indications for IFC:
- Acute or chronic pain
- Muscle spasms
- Joint and ligament injuries
d. Iontophoresis
This technique uses a small electrical charge to deliver medication (such as anti-inflammatory drugs) through the skin. It is used to treat localized inflammation, pain, and other conditions.
Indications for iontophoresis:
- Tendonitis
- Bursitis
- Inflammatory conditions
3. Ultrasound Therapy
a. Therapeutic Ultrasound
Therapeutic ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to penetrate deep into the tissues. The sound waves generate heat within the tissues, which can promote tissue healing, reduce muscle spasms, and improve blood flow. It can also be used for phonophoresis (delivering medication through the skin via ultrasound).
Indications for ultrasound therapy:
- Chronic musculoskeletal pain
- Soft tissue injuries (e.g., sprains, strains)
- Scar tissue and adhesions
- Tendonitis or bursitis
4. Laser Therapy (Low-Level Laser Therapy, LLLT)
Low-level laser therapy uses light energy to promote healing and reduce inflammation. The light energy is absorbed by tissues, enhancing cellular function and accelerating tissue repair.
Indications for laser therapy:
- Soft tissue injuries
- Chronic pain management
- Inflammatory conditions
- Wound healing
5. Traction Therapy
Traction is a technique used to relieve pressure on the spine or joints. It is applied mechanically or manually to stretch and decompress the affected area. It is commonly used for conditions like herniated discs, pinched nerves, and joint stiffness.
Indications for traction therapy:
- Spinal disc herniation or bulging discs
- Neck or back pain
- Sciatica
- Spinal stenosis
6. Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy involves the use of water (usually warm) to promote healing, relieve pain, and improve mobility. It can be delivered through:
- Aquatic therapy: Performing exercises in a pool to reduce weight-bearing stress on joints and improve mobility.
- Whirlpool baths: Submerging the body or a body part in warm water to relax muscles and reduce pain.
Indications for hydrotherapy:
- Joint rehabilitation (e.g., post-surgery)
- Arthritis
- Muscle relaxation and pain relief
- Improving balance and mobility
7. Biofeedback
Biofeedback uses sensors to monitor physiological functions such as heart rate, muscle tension, or skin temperature, and provides real-time feedback to the patient. The goal is to help the patient learn to control these physiological functions to reduce pain or stress.
Indications for biofeedback:
- Chronic pain (e.g., fibromyalgia, headaches)
- Stress and anxiety management
- Muscle tension and spasms
8. Infrared Therapy
Infrared therapy uses infrared light to increase circulation and promote healing in tissues. The light penetrates the skin to reach deeper tissues, warming them and increasing blood flow.
Indications for infrared therapy:
- Muscle pain and stiffness
- Joint pain (e.g., arthritis)
- Soft tissue injuries
Goals and Benefits of Physical Modalities:
- Pain Relief: Many modalities, such as heat, cold, and electrical stimulation, help reduce pain associated with acute or chronic conditions.
- Inflammation Control: Cold therapy and certain electrical modalities can help reduce swelling and inflammation after an injury or surgery.
- Muscle Relaxation: Techniques like heat therapy, electrical stimulation, and massage help reduce muscle tension and spasms.
- Healing Promotion: Modalities like ultrasound, laser therapy, and electrical stimulation can accelerate tissue healing by increasing blood flow, reducing inflammation, and promoting cellular repair.
- Improved Mobility: Heat, ultrasound, and hydrotherapy can help improve joint flexibility and muscle function, reducing stiffness.
In practice, physical modalities are often used in combination with other forms of treatment, such as exercises and manual therapy, to maximize the benefits and optimize recovery outcomes for patients.